
A robot is a machine, usually equipped with arms, wheels or legs, that operates automatically. The majority of robots are to be found in industries such as car manufacturing, where they are used to do tasks that would otherwise be dangerous, difficult or tedious for people. Recently personal robots for the home have become a reality, with the introduction of the Roomba vacuum cleaner and the RoboMower grass cutter. These robots are relatively simple and are a long way from the robot helpers we see in films such as Star Wars and Wall.e. The largest growth areas in robotics over the last 10 years has been entertainment and education. Robot pets often called ‘cyber pets’ have been hugely popular and many colleges and universities have been using robotic kits, such as the Lego NXT Mindstorm, to teach students about robotics and engineering principles.
Robot Fundamentals
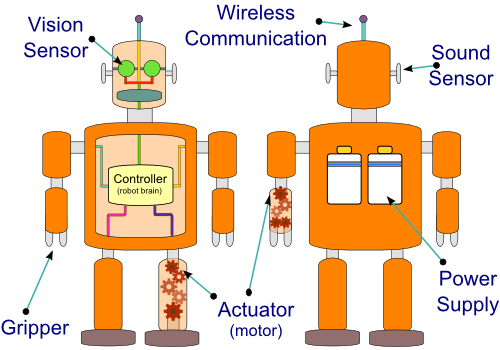
The above diagram shows a robot modelled on a human, often referred to as a humanoid. As you can see there are many parts that make up a robot, each of which can be designed in different ways depending on the purpose of the robot. The following sections will discuss these design considerations.A downloadable guide to Robotics can be found here.
Sensors
Lego NXT sensors |
Multi-sensor mobile robot |
Ultrasonic sensor module |
Robot sensors can be compared to our eyes, ears and sense of touch. Without sensors a robot has no way of perceiving its environment and can only perform predetermined tasks. There are two main types of sensors, those that sense the external world and those that sense the internal state of the robot. The following is a list of popular robot sensors:
External
- Light Sensor
- Often in the form of a light dependant resistor (LDR), depending on the intensity of the light, the resistance in the circuit changes. This can be used to sense the direction of a light source.
- Contact Sensor
- Proximity Sensor
Internal
- Gyro – Used to keep the robot balanced
- Accelerometer – For measuring movement
- Temperature – For regulating the internal temperature of the robot
Tools and Attachments
Space shuttle manipulator |
Robot gripper |
Early robot with packaging tool |
In robotics the tool or attachment at the end of a robotic arm is called an end effector. This end effector is used to interact with the environment, allowing the robot to carry out its task. The selection of the tool/attachment is dependent on the application of the robot; for example, robots used in car manufacturing often have interchangeable tools allowing the robot to complete various tasks, such as welding and paint spraying. Another example, often found in mobile Robots, is that of a universal-gripper, this type of attachment is much like a human hand and can be used to perform a variety of tasks such as picking-up objects, opening doors or pushing a switch.
Different Types of Robots
There are many different types of robots each designed for a specific task. Generally robots can be divided into two categories, those that operate in a fixed position and those that are mobile. Fixed robots are those which are anchored to a point and use manipulators such as arms to complete tasks. Many examples of fixed robots can be found in manufacturing where they are used for a variety of purposes, such as spray painting, welding, assembly and quality control. Mobile robots are designed to move around their environment using one or more wheels, legs or tracks, depending on the intended operating surface. The following is a list of the types of robots currently in use:
- Industrial robots
- Space rovers
- Bomb disposal
- Robotic surgery
- Automated guided vehicle (AGV)
- Autonomous underwater vehicle(AUV)
- Entertainment
- Military – Reconnaissance
To Read More About Robotics, Click Here »
State of the Art Robots
To read about the latest Robots such as Honda’s ASIMO, Toyota’s Partner, PaPeRo the Personal Robot and many more take a look at our Robots page by clicking here.









